Types Of Hacking Attacks
1.1 Denial of Service Attacks
- The first type of attack to examine is the denial of service (DoS). A denial of service attack is any attack that aims to deny legitimate users of the use of the target system. This class of attack does not actually attempt to infiltrate a system or to obtain sensitive information. It simply aims to prevent legitimate users from accessing a given system.
- This type of attack is one of the most common categories of attack. Many experts feel that it is so common because most forms of denial of service attacks are fairly easy to execute. The ease with which these attacks can be executed means that even attackers with minimal technical skills can often successfully perform a denial of service.
- The concept underlying the denial of service attack is based on the fact that any device has operational limits. This fact applies to all devices, not just computer systems. For example, bridges are designed to hold weight up to a certain limit, aircraft have limits on how far they can travel without refuelling, and automobiles can only accelerate to a certain point. All of these various devices share a common trait: They have set limitations to their capacity to perform work. Computers are no different from these, or any other machine; they, too, have limits. Any computer system, web server, or network can only handle a finite load.
- How a workload (and its limits) is defined varies from one machine to another. A workload for a computer system might be defined in a number of different ways, including the number of simultaneous users, the size of files, the speed of data transmission, or the amount of data stored. Exceeding any of these limits will stop the system from responding. For example, if you can flood a web server with more requests than it can process, it will be overloaded and will no longer be able to respond to further requests. This reality underlies the DoS attack. Simply overload the system with requests, and it will no longer be able to respond to legitimate users attempting to access the web server.
1.2 SYN Flood
- Simply sending a flood of pings is the most primitive method of performing a DoS. More sophisticated methods use specific types of packets. One popular version of the DoS attack is the SYN flood. This particular attack depends on the hacker’s knowledge of how connections are made to a server. When a session is initiated between the client and server in a network using the TCP protocol, a small buffer space in memory is set aside on the server to handle the “hand-shaking” exchange of messages that sets up the session. The session-establishing packets include a SYN field that identifies the sequence in the message exchange.
- A SYN flood attempts to disrupt this process. In this attack, an attacker sends a number of connection requests very rapidly and then fails to respond to the reply that is sent back by the server. In other words, the attacker requests connections, and then never follows through with the rest of the connection sequence. This has the effect of leaving connections on the server half open, and the buffer memory allocated for them is reserved and not available to other applications. Although the packet in the buffer is dropped after a certain period of time (usually about three minutes) without a reply, the effect of many of these false connection requests is to make it difficult for legitimate requests for a session to be established.
1.3 Smurf Attack
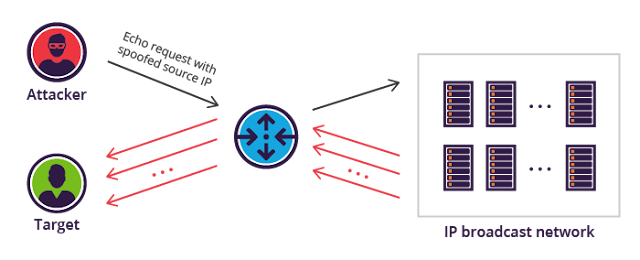
- The Smurf attack is a popular type of DoS attack. It was named after the application first used to execute this attack. In the Smurf attack, an ICMP packet is sent out to the broadcast address of a network, but its return address has been altered to match one of the computers on that network, most likely a key server. All the computers on the network will then respond by pinging the target computer.
- ICMP packets use the Internet Control Message Protocol to send error messages on the Internet. Because the address of packets are sent to is a broadcast address, that address responds by echoing the packet out to all hosts on the network, who then send it to the spoofed source address.
- Continually sending such packets will cause the network itself to perform a DoS attack on one or more of its member servers. This attack is both clever and simple. The greatest difficulty is getting the packets started on the target network. This can be accomplished via some software such as a virus or Trojan horse that will begin sending the packets.
1.4 Ping of Death
- The Pingof Death (PoD), is perhaps the simplest and most primitive form of DoS attack and is based on overloading the target system. TCP packets have limited size. In some cases by simply sending a packet that is too large, can shut down a target machine.
- The aim of this attack is to overload the target system and cause it to quit responding. The PoD works to compromise systems that cannot deal with extremely large packet sizes. If successful, the server will actually shut down. It can, of course, be rebooted.
- The only real safeguard against this type of attack is to ensure that all operating systems and software are routinely patched. This attack relies on vulnerabilities in the way a particular operating system or application handles abnormally large TCP packets. When such vulnerabilities are discovered, the vendor customarily releases a patch. The possibility of PoD is one reason, among many, why you must keep patches updated on all of your systems.
- This attack is becoming less common as newer versions of operating systems are better able to handle the overly large packets that Ping of Death depends on. If the operating system is properly designed, it will drop any oversized packets, thus negating any possible negative effects a PoD attack might have.
1.5 UDP Flood
- UDP (UserDatagram Protocol) is a connection less protocol and it does not require any connection setup procedure to transfer data. TCP packets connect and wait for the recipient to acknowledge receipt before sending the next packet. Each packet is confirmed. UDP packets simply send the packets without confirmation. This allows packets to be sent much faster, making it easier to perform a DoS attack.
- A UDP flood attack occurs when an attacker sends a UDP packet to a random port on the victim system. When the victim system receives a UDP packet, it will determine what application is waiting on the destination port. When it realizes that no application is waiting on the port, it will generate an ICMP packet of destination unreachable to the forged source address. If enough UDP packets are delivered to ports on the victim, the system goes down.
1.6 DoS Tools
- One reason that DoS attacks are becoming so common is that a number of tools are available for executing DoS attacks. These tools are widely available on the Internet, and in most cases are free to download. This means that any cautious administrator should be aware of them. In addition to their obvious use as an attack tool, they can also be useful for testing your anti-DoS security measures.
- Low Orbit Ion Cannon (LOIC) is probably the most well know and one of the simplest DoS tool. You first put the URL or IP address into the target box. Then click the Lock On button. You can change settings regarding what method you choose, the speed, how many threads, and whether or not to wait for a reply. Then simply click the IMMA CHARGIN MAH LAZER button and the attack is underway.
- High Orbit Ion Cannon (HOIC) is a bit more advanced than LOIC, but actually simpler to run. Click the + button to add targets. A popup window will appear where you put in the URL as well as a few settings.
1.7 Buffer Overflow Attacks
- Another way of attacking a system is called a buffer overflow (or buffer overrun) attack. Some experts would argue that the buffer overflow occurs as often as the DoS attack, but this is less true now than it was a few years ago. A buffer overflow attack is designed to put more data in a buffer than the buffer was designed to hold. This means that although this threat might be less than it once was, it is still a very real threat.
- Any program that communicates with the Internet or a private network must receive some data. This data is stored, at least temporarily, in a space in memory called a buffer. If the programmer who wrote the application was careful, the buffer will truncate or reject any information that exceeds the buffer limit.
- Given the number of applications that might be running on a target system and the number of buffers in each application, the chance of having at least one buffer that was not written properly is significant enough to cause any cautious system administrator some concern. A person moderately skilled in programming can write a program that purposefully writes more data into the buffer than it can hold. For example, if the buffer can hold 1024 bytes of data and you try to fill it with 2048 bytes, the extra 1024 bytes is then simply loaded into memory.
- If the extra data is actually a malicious program, then it has just been loaded into memory and is running on the target system. Or perhaps the perpetrator simply wants to flood the target machine’s memory, thus overwriting other items that are currently in memory and causing them to crash. Either way, the buffer overflow is a very serious attack.
- Fortunately, buffer overflow attacks are a bit harder to execute than the DoS or a simple MS Outlook script virus. To create a buffer overflow attack, a hacker must have a good working knowledge of some programming language (C or C++ is often chosen) and understand the target operating system/application well enough to know whether it has a buffer overflow weakness and how it might exploit the weakness.
1.8 IP Spoofing
- IP spoofing is essentially a technique used by hackers to gain unauthorized access to computers. Although this is the most common reason for IP spoofing, it is occasionally done simply to mask the origins of a DoS attack. In fact DoS attacks often mask the actual IP address from which the attack is originating.
- With IP spoofing, the intruder sends messages to a computer system with an IP address indicating that the message is coming from a different IP address than it is actually coming from. If the intent is to gain unauthorized access, then the spoofed IP address will be that of a system the target considers a trusted host.
- To successfully perpetrate an IP spoofing attack, the hacker must first find the IP address of a machine that the target system considers a trusted source. Hackers might employ a variety of techniques to find an IP address of a trusted host. After they have that trusted IP address, they can then modify the packet headers of their transmissions so it appears that the packets are coming from that host.
- IP spoofing, unlike many other types of attacks, was actually known to security experts on a theoretical level before it was ever used in a real attack. The concept of IP spoofing was initially discussed in academic circles as early as the 1980s. Although the concept behind this technique was known for some time, it was primarily theoretical until Robert Morris discovered a security weakness in the TCP protocol known as sequence prediction.
- IP spoofing attacks are becoming less frequent, primarily because the venues they use are becoming more secure and in some cases are simply no longer used. However, spoofing can still be used, and all security administrators should address it.
A couple of different ways to address IP spoofing include:
- Do not reveal any information regarding your
internal IP addresses. This helps prevent those addresses from being
“spoofed.”
- Monitor incoming IP packets for signs of IP spoofing
using network monitoring software. One popular product is Netlog. This and
similar products seek incoming packets to the external interface that have
both the source and destination IP addresses in your local domain, which
essentially means an incoming packet that claims to be from inside the
network, when it is clearly coming from outside your network. Finding one
means an attack is underway.
Examples of router configurations that are potentially vulnerable include:
- Routers to external networks that support
multiple internal interfaces
- Proxy firewalls where the proxy applications use
the source IP address for authentication
- Routers with two interfaces that support
subnetting on the internal network
- Routers that do not filter packets whose source
address is in the local domain
1.9 Guided Exercise: Preventing IP Spoofing
Resources
|
|
Files
|
None
|
Machines
|
Ubuntu
Server
|
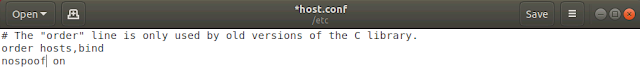
Login to Ubuntu Server and once logged in run the command “sudo gedit /etc/host.conf”. Sudo will ask the user password and enter “Pa$$w0rd”. The host configuration file will open. The host.conf configuration file contains configuration information specific to the resolver library
Make the changes shown in the screenshot below which you simply change the word multi to nospoof.
By adding the value nospoof on the resolver library will attempt to prevent hostname spoofing for enhanced security.
After making the changes press SAVE to to save the changes and then close the file.
2.0 Session Hijacking
- Another form of attack is session hacking or hijacking. TCP session hijacking is a process where a hacker takes over a TCP session between two machines. Because authentication frequently is done only at the start of a TCP session, this allows the hacker to break into the communication stream and take control of the session. For example, a person might log on to a machine remotely. After establishing a connection with the host, the hacker might use session hacking to take over that session and thereby gain access to the target machine.
- One popular method for session hacking is using source-routed IP packets. This allows a hacker at point A on the network to participate in a conversation between B and C by encouraging the IP packets to pass through the hacker’s machine.
- The most common sort of session hacking is the “man-in-the-middle attack.” In this scenario, a hacker uses some sort of packet-sniffing program to simply listen the transmissions between two computers, taking whatever information he or she wants but not actually disrupting the conversation. A common component of such an attack is to execute a DoS attack against one end point to stop it from responding. Because that end point is no longer responding, the hacker can now interject his own machine to stand in for that end point.
- The point of hijacking a connection is to exploit trust and to gain access to a system to which one would not otherwise have access.
I Hope you find this article informative. If you have any queries than do let us know in the comments section below and we would love to get back to you at the earliest.
Thank you for read this article... SUBSCRIBE OUR BLOG FOR LATEST POST.
Sagar IT World
Your Solution We Provide












0 Comments
For More Information Please Comment