Computer Networking Fundamental
A computer network is a network of computers that are geographically distributed, but connected in a manner to enable meaningful transmission and exchange of data among them. Sharing of information, resources (both hardware and software), and processing load is the main objective of a computer networking.
Three basic elements of any communication system are a sender (source) that creates and sends a message, a medium that carries the message, and a receiver (sink) the receives the message.
Computer Networks use a concept of layered protocols. The OSI model provides a standard for layered protocols for WANs. The seven layers of the OSI model are physical, data-link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application. Of the available protocol suites for network systems, the Internet Protocol (IP) suite is the most popular and widely used.
Growth of computer networking
The growth and uses of the global Internet† are among the most interesting and exciting phenomena in networking. In 1980, the Internet was a research project that involved a few dozen sites. Today, the Internet has grown into a production communication system that reaches all populated countries of the world. Many users have highspeed Internet access through cable modems, DSL, or wireless technologies.
Computer networking has grown explosively. Since the 1970s, computer communication has changed from an esoteric research topic to an essential part of the infrastructure. Networking is used in every aspect of business, including advertising, production,
shipping, planning, billing, and accounting. Consequently, most corporations have multiple networks. Schools, at all grade levels from elementary through post-graduate, are
using computer networks to provide students and teachers with instantaneous access to
online information. Federal, state, and local government offices use networks, as do
military organizations. In short, computer networks are everywhere.
Computer networking has grown explosively. Since the 1970s, computer communication has changed from an esoteric research topic to an essential part of the infrastructure. Networking is used in every aspect of business, including advertising, production,
shipping, planning, billing, and accounting. Consequently, most corporations have multiple networks. Schools, at all grade levels from elementary through post-graduate, are
using computer networks to provide students and teachers with instantaneous access to
online information. Federal, state, and local government offices use networks, as do
military organizations. In short, computer networks are everywhere.
Network Types:
PAN:- personal area network
LAN:- local area network
MAN:- metropolitan area network
WAN:- wide area network
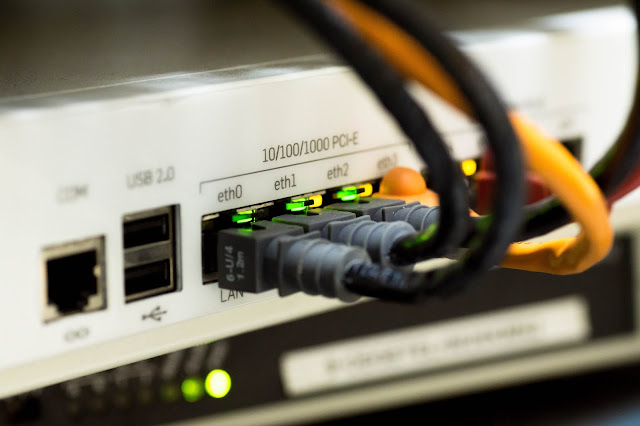
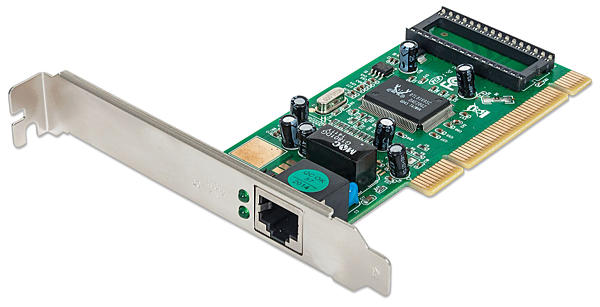
Network Interface Card (NIC)
network interface card, often referred to as NIC or network card, is a hardware device that connects a computer to a network, both functionally and physically. It is a printed circuit board (PCB), which connects to one of the expansion slots of a computer, and provides a port for attaching a network cable. It is an add-on card (expansion board) connected directly to a computer's I/O bus.
Since an NIC connects directly to a computer's I/O bus, design of an NIC is specific to a computer's I/O bus hardware, computer's operating system, and network's communication protocol. NIC's ROM has the network's physical-layer communication protocol. Hence, there are different NICs for different networks, even for same computer. For example, to connect a computer to an Ethernet LAN,it must have an Ethernet network network card, and to connect it to an ATM network, it must have an ATM network card.
Introduction to IP Addresses
IP = Internet Protocol Address
IP address. An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. Basically 2 types of version of IP Addresses
First: IPv4 Internet protocol version 4
Second: IPv6 Internet protocol version 6
Difference Between IPv4 AND IPv6
Internet Protocol Version 4
- IPv4 offers 12 header fields
- IPv4 binary bits are separated by a dot(.)
- IPv4 is 32 bit IP address
- IPv4 supports broadcast
- IPv4 is a numeric addressing method
- IPv4 supports VLSM (virtual length subnet mask)
- IPv4 has checksum fields
- IPv4 uses ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) to map to MAC address
Internet Protocol Version 6
- IPv6 offers 8 header fields
- IPv6 binary bits are separated by a colon(:)
- IPv6 is a 128 bit IP address
- IPv6 does not support broadcast
- IPv6 is an alphanumeric addressing method
- IPv6 does not support VLSM
- IPv6 does not have checksum fields
- IPv6 uses NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) to map to MAC address.
How to find Internet Protocol (IP) Address in your computer
- press window+r in your computer
- type cmd & press enter
- then Command Prompt screen will be appear in your computer
- type command: ipconfig and press enter.
I Hope you like this article Thanks for read this article.
Please share this article to your friends and family members..
subscribe to our blog for more articles...









0 Comments
For More Information Please Comment